Scrum Methodology – An Overview
Principles of Scrum:
- Process Control: Scrum operates on the principles of transparency, inspection, and adaptation. Thus, teams regularly inspect their work and adapt their processes based on feedback and new information.
- Iterative Development: Furthermore, Scrum methodology divides the project into small, manageable iterations called sprints, typically lasting 2-4 weeks. Each sprint results in a potentially shippable product increment, allowing for rapid feedback and course correction.
- Self-Organizing Teams: Scrum teams are cross-functional and self-organizing to determine how best to accomplish their goals. Therefore, team members collaborate closely and collectively take ownership of the project.
Roles in Scrum approach:
- Product Owner: Represents the stakeholders and communicates their requirements to the development team. Prioritizes the product backlog and ensures that the team delivers value that aligns with the overall vision and goals.
- Scrum Master: The Scrum master facilitates the Scrum process, removes impediments, and ensures that the team adheres to Scrum values and practices. It acts as a servant-leader, coaching the team to maximize productivity and effectiveness.
- Development Team: Cross-functional group responsible for delivering the product increment. Self-organizes and collaborates to complete the work defined in the sprint backlog.
Is Scrum agile methodology?
Yes, Scrum methodology is an agile technique. Indeed, it is one of the most extensively used agile frameworks.
The agile approach, in general, refers to a set of ideas and ideals described in the Agile Manifesto that favor persons and relationships, functioning products, customer collaboration, and adapting to change.
Scrum embodies the agile ideals of iterative development, continuous feedback, and tight communication among team members and stakeholders. It stresses adaptability, flexibility, and customer-centricity, enabling teams to create value gradually while responding swiftly to changing requirements and priorities.
By adopting Scrum, teams may leverage the power of agility to simplify their processes, improve transparency, and create high-quality products or solutions.
Scrum – Pros and Cons
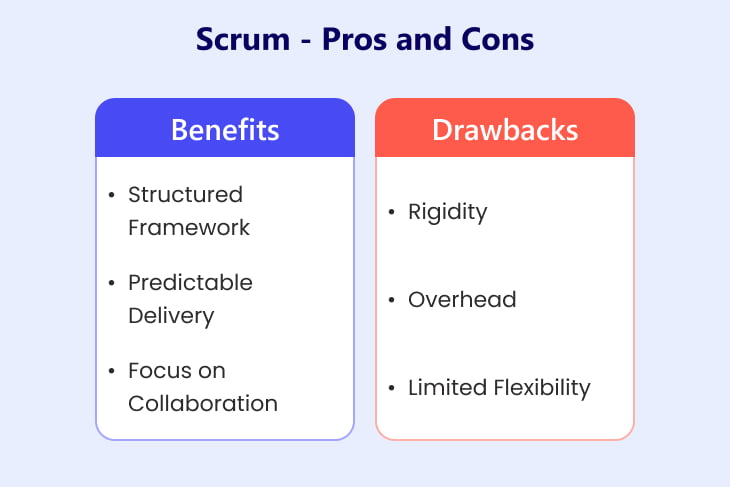
Let’s know the benefits of the Scrum in detail:
- Structured Framework: Scrum provides a well-defined framework with clear roles, offering teams a structured approach to project management. Moreover, this structure promotes transparency, accountability, and collaboration, enabling teams to work cohesively towards common goals.
- Predictable Delivery: Scrum’s sprints, facilitate predictable delivery cycles, allowing teams to plan and forecast with greater accuracy.
- Focus on Collaboration: Scrum emphasizes cross-functional collaboration and regular communication, fostering a sense of ownership and collective responsibility within the team.
Drawbacks of Scrum Methodology
Now you know the benefits of Scrum, let’s understand the drawbacks in detail:
- Rigidity: Strict adherence to roles and time-based iterations may destroy creativity and innovation, especially in dynamic or unpredictable environments.
- Overhead: Scrum requires dedicated roles, such as Scrum Master and Product Owner, and regular tasks, such as sprint planning and retrospectives, which may introduce overhead and administrative burden, particularly for small teams or short-duration projects.
- Limited Flexibility: Scrum’s fixed-length sprints and prioritized backlogs may limit flexibility for teams facing rapidly changing requirements or priorities. Adapting to unexpected changes mid-sprint can be challenging, potentially leading to delays or compromises in quality.
Tools used in Scrum methodology
There are various scrum methodology tools available in the market. One of the best is Alian Hub. It is a comprehensive project management system that offers management, collaboration, and analytical features to deliver projects effectively.
This tool is best for Scrum because it allows project managers to handle projects by creating sprints, setting priorities, assigning members, estimating time, and more. Project managers can easily track the workload of their team members by workload view & reports.
Moreover, it comes with a free time tracker that monitors user actions by counting mouse and keyboard keystrokes and capturing screenshots of work in progress. Thus, a Scrum Team can manage multiple projects and deliver them on time.
Conclusion
While Scrum has various advantages, such as defined frameworks, consistent delivery, and a focus on collaboration, it also has negatives, including rigidity, overhead, and restricted adaptability. Understanding these advantages and disadvantages is critical for teams to successfully follow Scrum methodology in their projects.
Furthermore, using solutions like Alian Hub may simplify Scrum deployment and improve project management skills, allowing teams to manage projects more efficiently and on schedule.
To summarize, Scrum methodology provides an effective framework for agile project management, allowing teams to handle complicated projects with agility, efficiency, and cooperation.

